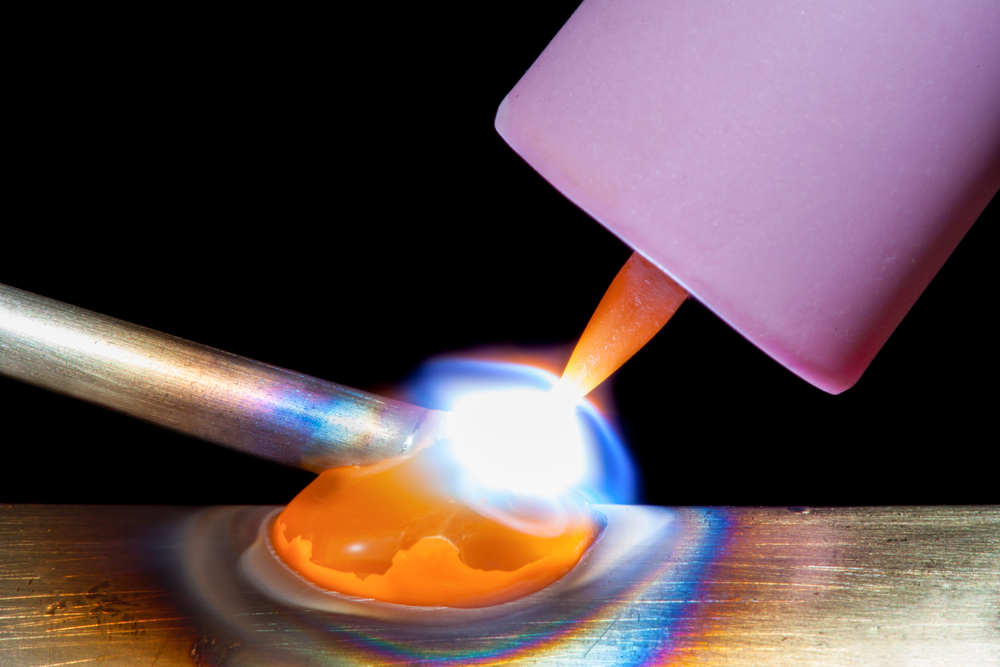
What is the Role of Shielding Gas in Welding?
November 12, 2024 4:40 pm Leave your thoughtsIn the world of welding, shielding gas is a vital component for creating strong, high-quality welds. Whether you’re a professional in welding shops or a DIY gas welder, understanding the role of shielding gas can significantly improve your welding results. Shielding gases are used to protect the weld area from contaminants and influence the weld’s final properties. This article dives deep into the importance of shielding gases, their types, and how to choose the right one for your welding needs.
Why is Shielding Gas Important in Welding?
Shielding gas plays a fundamental role in the welding process by providing a protective barrier between the molten weld pool and the atmosphere. Without shielding gas, atmospheric gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen can easily react with the molten metal, leading to weld defects such as porosity, cracking, and oxidation. These issues compromise the structural integrity and appearance of the weld, making shielding gas crucial for high-quality, durable welds.
Using the right shielding gas helps control the weld’s heat distribution, penetration, and appearance. It can also impact factors like arc stability, spatter levels, and metal transfer modes, all of which directly influence the ease and effectiveness of the welding process in both professional and home welding setups.
Types of Shielding Gases
Selecting the appropriate shielding gas depends on the type of metal you’re working with, the welding process, and the desired weld characteristics. There are several commonly used shielding gases in welding, each with unique properties that make them suitable for specific applications.
Argon (Ar)
Argon is a widely used shielding gas, particularly in gas metal arc welding (GMAW) and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). Its inert properties make it ideal for protecting the weld pool without reacting with it, and it creates a smooth, stable arc. Argon is especially effective for welding non-ferrous metals like aluminum, magnesium, and copper.
Argon provides:
- Improved arc stability
- Reduced spatter
- Better weld appearance
However, for steel welding, pure argon is generally used in combination with other gases to avoid issues with penetration and weld quality.
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Carbon dioxide is commonly used in gas welding for its affordability and effectiveness. Pure CO₂ is often used in gas metal arc welding (GMAW) for carbon steel. However, it tends to produce more spatter compared to other shielding gases.
Advantages of CO₂ include:
- Deeper weld penetration
- Cost-effectiveness
- Ideal for thicker materials
However, its reactive nature can cause oxidation in the weld, and it isn’t suitable for non-ferrous metals. CO₂ is often mixed with argon in gas welding to balance penetration and reduce spatter.
Argon-CO₂ Mix
A blend of argon and CO₂ is often used in welding shops to provide the benefits of both gases. A common mixture is 75% argon and 25% CO₂, which combines the smooth arc of argon with the deeper penetration of CO₂, resulting in a cleaner weld with fewer spatter issues. This blend is popular for welding mild steel and offers a good balance between weld quality and cost-effectiveness.
Helium (He)
Helium is another inert gas often used as a shielding gas, especially for materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. Helium is more expensive than other gases but provides hotter arcs, which allows for faster welding speeds and deeper penetration. Helium is often mixed with argon in various ratios, depending on the desired weld characteristics.
Helium is ideal for:
- Thick materials
- High heat conductivity metals
- Faster welding speeds
Because helium is less dense than argon, higher flow rates are required to achieve effective shielding, which can make it more costly for extensive projects.
Oxygen (O₂) and Nitrogen (N₂)
Oxygen and nitrogen are sometimes added in small percentages (usually 1–5%) to other gases to improve weld characteristics. For example, adding a small amount of oxygen to argon can enhance arc stability and improve penetration, especially in steel welding. Nitrogen, on the other hand, is more specialized, often used for stainless steel and other alloys to improve corrosion resistance.
How to Choose the Right Shielding Gas
Choosing the correct shielding gas is essential for achieving optimal weld quality, and it depends on several factors, including the welding process, the type of metal, and the desired characteristics of the weld.
Welding Process
Each welding process has specific requirements for shielding gases. For example, MIG welding often utilizes a mix of argon and CO₂, while TIG welding typically uses pure argon. Stick welding, on the other hand, generally doesn’t require shielding gas as the electrode coating provides protection.
Understanding which gas pairs best with each welding method can save both time and money in the welding shop and improve the quality of the finished product.
Material Type
Different materials require specific shielding gases for optimal results:
- Steel: For carbon steel, a mix of argon and CO₂ is often used to balance cost and performance. Stainless steel welding might require a mixture of argon with CO₂ or even a small amount of oxygen.
- Aluminum and Magnesium: Pure argon or a mix of argon with helium works best for these non-ferrous metals to avoid contamination and achieve a smooth weld.
- Copper and Bronze: Helium or a helium-argon mix provides the high heat needed for welding these metals effectively.
Weld Appearance and Penetration Requirements
Some welding jobs require deep penetration, while others prioritize a clean, visually appealing weld. Helium is beneficial for deeper penetration, while argon provides smoother, more aesthetic welds. The ratio of CO₂ in an argon mix can also affect penetration and spatter levels, allowing welders to fine-tune the gas selection based on specific job requirements.
Shielding Gas Safety and Handling Tips
Handling and storing shielding gases requires attention to safety, especially in welding shops where gas cylinders are common. Here are some key safety tips:
- Proper Storage: Store gas cylinders upright and secure them to prevent falling. Avoid direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Cylinder Handling: Use a cylinder cart to transport gas cylinders and always wear protective gloves when handling them.
- Regulator Maintenance: Regularly inspect gas regulators and connections for leaks. A small leak can lead to wasted gas, and in the case of flammable gases, it could pose a safety hazard.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in the welding area to prevent gas buildup, which can be hazardous to health and safety.
Following these guidelines can help protect both welders and the work environment.
The Role of Shielding Gas in Different Welding Environments
The choice of shielding gas varies significantly between professional welding shops and individual gas welder setups. In a welding shop, it’s common to find a variety of gas mixes on hand, as different projects may call for different gases to achieve the best results. Experienced welders in these shops can adjust the gas mix to meet specific project requirements.
For DIY or home welding, cost and simplicity often influence gas selection. Many home gas welders prefer a CO₂-argon mix, which is versatile and works well on a range of mild steel applications. While pure CO₂ is the most affordable option, welders may opt for mixed gases to achieve cleaner, less porous welds.
The Essential Role of Shielding Gas in Welding
Shielding gas is a cornerstone of quality welding, offering both protection and control over the welding process. From enhancing arc stability to preventing oxidation, shielding gas impacts every aspect of weld quality and durability. In welding shops and individual gas welding setups, choosing the right shielding gas can make the difference between a strong, smooth weld and one riddled with defects.
Whether you are a professional welder or a hobbyist, understanding the properties of shielding gases can help you produce cleaner, stronger welds tailored to your specific needs. The investment in proper shielding gas pays off in improved weld quality, fewer repairs, and a more efficient welding process overall.
Need Steel Fabricators in Hermiston, OR?
NW Metal Fabricators, Inc. is a family-owned business that has been servicing customers in Hermiston, Oregon since 1986. We have more than 100 years of experience in the food-processing industry and specialize in the custom production of storage bins, conveyors, catwalks, handrails, gates, storage tanks, water heater tanks, sanitary piping, steam piping, and trailer truck hitches. NW Metal Fabricators, Inc. is an accredited member of the local Chamber of Commerce. We are a dedicated business where quality always comes first. Our customers know that they can count on us to make sure that their products are hand-crafted to meet their specifications. Contact us today to learn more about what we can do for you!
Categorised in: Welding
This post was written by admin
